The clotting of the blood is essential in ensuring that excessive loss of blood can be avoided. The process takes place with the help of a blood component called platelets.
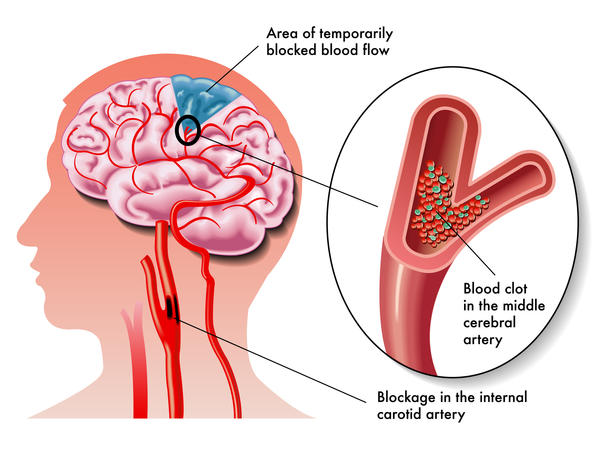
Blood clotting is a normal response to injury in order to protect the body against the complications that can result from excessive blood loss. However, in some cases, a blood clot abnormally develops in blood vessels, causing an interference in the flow of blood to some parts of the body.
When a blood vessel is blocked, essential factors like oxygen and nutrients needed for normal functioning of the recipient body organ will not be fully provided. The shortage of oxygen and nutrients can further lead to complications with adverse severity.
For instance, the brain has a control of every activity carried out in the body. A failure to function due to lack of oxygen in the brain can affect the functioning of the whole body.
A blood clot can be formed in the arteries that directly supply blood to the brain. It may also form in other areas of the body but can suddenly dislodge and move along with the blood towards the arteries of the brain, causing a blockage against flowing blood.
The blockage is a well-known primary cause of stroke as observed among most patients.
Common signs and symptoms of blood clot in brain
1. Recurring headaches
There are several causes for the onset of headaches in a person. It is also possible for some headaches to occur without any obvious reason.
When headaches occur recurrently without being triggered by any known reason, it may be associated with formation of a blood clot in the brain.
A blood clot in brain can result to increased pressure exerted within the arteries due to blood accumulation trying to pass through the blocked arteries.
2. Problems with speech
A blood clot can lead to insufficient oxygen supply to different parts of the brain.
The location of the artery affected will have a specific influence on the brain. This is to say that impairment in the functioning mainly depends on the part of the brain affected.
Since different parts of the brain carry out different tasks, the role played by the affected part of the brain will be altered.
In some cases, the speech of the patient becomes slurred or garbled. In this event, the speech coordinators of the brain is the area that is likely affected.
3. Paralysis
Paralysis is a common symptom of stroke which is mainly caused by a clot in the brain of the patient.
In some cases, failure of the brain to receive enough oxygen can result to the paralysis of some body parts.
Commonly, the arms, face, and legs are the areas mostly affected. They will display a loss of normal sensory and/or motor function.
4. Depression
This can happen when a person is diagnosed with a blood clot, especially if the clot is life-threatening and extensive. However, depression is an emotional state that can affect the outcome of medical treatment.
It is normal to feel anxious, shocked, and fearful following the diagnosis of a blood clot.
5. Confusion
Thought processes and understanding are some of the main activities coordinated in the brain. When the brain is blocked from receiving enough oxygen, normal activities will be compromised.
A patient who is confused due to insufficient oxygen in the brain will behave as if they cannot understand any single word; or it takes too long for the person to reason and comprehend. This also happens even when given with very simple instructions that is easily understood.
6. Vision problems
A blood clot in the brain can result to an inability to see properly due to visual functions being tampered.
The area of the brain involved with vision processes (the occipital lobe) becomes unable in its position to function normally due to the lack of oxygen. This causes the individual to experience blurry or double vision.
In some cases, the patient may experience tunnel vision as well as complete inability to see. The patient may also lose the ability of sight in one eye but still be able to see with the other eye.
7. Poor coordination
Body coordination of a person depends greatly on the functionality of the brain. The impairment of the brain can affect the brain’s ability to coordinate normal body activities such as movement.
When cells of the brain lack a supply of oxygen, they can become sluggish or worse, if the cells do not receive any oxygen at all, they could die.
If the body parts involved in coordination are sluggish or denatured, there will also be a loss of balance. In extreme cases, there will be no visible coordination at all.
8. Ischemic attack
When one side of the brain is deprived of oxygen, it implies that only one side of the body will experience dysfunction. The condition is referred to as hemiplegia.
If this type of stroke is not managed, it may escalate, possibly leading to dysfunction of the whole body.
9. Increased heart rate
Any disorder in the functioning of the body will be normally addressed by body mechanisms to try and rectify the problem.
Since the brain controls most of the metabolic activities in the body, any alterations in its functioning will create a signal of distress. The shortage in the supply of oxygen to the brain will result to an increased heartbeat with the aim of offsetting the imbalance.
The brain will command the heart muscles to increase the rate of expansions and contractions in order to make sure that enough oxygen reaches the brain.
10. Rupture of veins
In extreme cases, the blood collected in the blocked blood vessels may lead to a rupturing of the vessels itself. This is due to the pressure exerted on the walls of the blood vessels.
The rupture may lead to complications to the extent that it may lead to death.
The brain is a major and very important part of the human body. Conditions that render it ineffective in carrying out its functions should be given attention at any cost.
Notes:
- The presence of a blood clot in the brain is a major risk factor for stroke
- The brain needs oxygen in order to perform its functions properly
- Brain failure can result to the loss of function of the different parts of the body
- Coordination is one of the main functions of the brain that commonly becomes altered as a complication of blood clot in brain
- READ MORE



I know I have a Blood Clot in my brain, it’s on the right side
right above my right eye but it does move from time to time and
at one time I had a severe headache all day then when I got home
in my garage the minute I stopped out of my truck the blood clot broke
loose and lodged in another part of my brain sending me into a seizure
Tests were done at the hospital ct/mri scan with contrast and yes, I was
told I had a brain blood clot but the VA Hospital in Palo Alto, CA said
I did not. Since then these constant feels like a very bad bee sting happens
over my right eye and lately have been happening constantly I am afraid
this will cause me to loose my life but the doctors at the VA Hospital do not do
anything say I do not have a blood clot yet tests were performed at a major
hospital with contrast and proved to be conclusive that I do have a BLOOD CLOT
IN MY BRAIN.