Blood clotting is a helpful normal body process when it occurs for the right reason at the right place. The presence of blood clots is beneficial only when it forms on the surface of damaged blood vessels in response to injury, with the aim to stop bleeding. What Causes Blood Clots in Lungs There are several … Continue reading “10 Signs of Blood Clot in Lung”
Normal functioning of the body includes proper response to blood vessel injury where a series of mechanisms result to the formation of blood clots on the surface of the damaged blood vessel. This process is initiated by a blood component called platelets.

There are two classifications of human veins in terms of closeness to the surface of the body: the superficial vein and the deep vein. The superficial vein can be easily traced, unlike the deep vein which is located deep in the body. The deep venous system is a common site for the development of blood … Continue reading “10 Best Food & Diet Meal Plan for Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)”

Blood Thinner Medications Blood thinners are commonly used in reducing the risk of stroke and heart attack that works by decreasing the formation of blood clots in arteries and veins of the body. Blood thinner meds may be advised by a doctor in patients with abnormal heart rhythms as seen in atrial fibrillation, heart valve … Continue reading “10 Blood Thinners and How They Work”
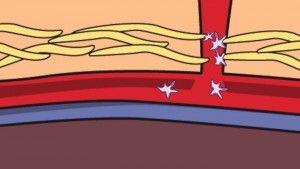
Platelets function in the control of bleeding by clogging and clumping in response to blood vessel that has been injured. The blood component perform the role during the blood clotting process with the help of other coagulation factors within the blood system.

Platelets play a critical role in the blood clotting process. The number of platelets in the blood is referred to as platelet count and normally ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 per one millionth of a liter of blood.
A low MPV with a low platelet count in the bloodstream can develop secondary to specific medical or hereditary reasons. When this happens, the number of platelets in the blood is considerably lower than levels normally needed by the body. It increases the risk of bleeding considering that platelets are responsible in blood clot formation.